Flour Fortification
₹600.00
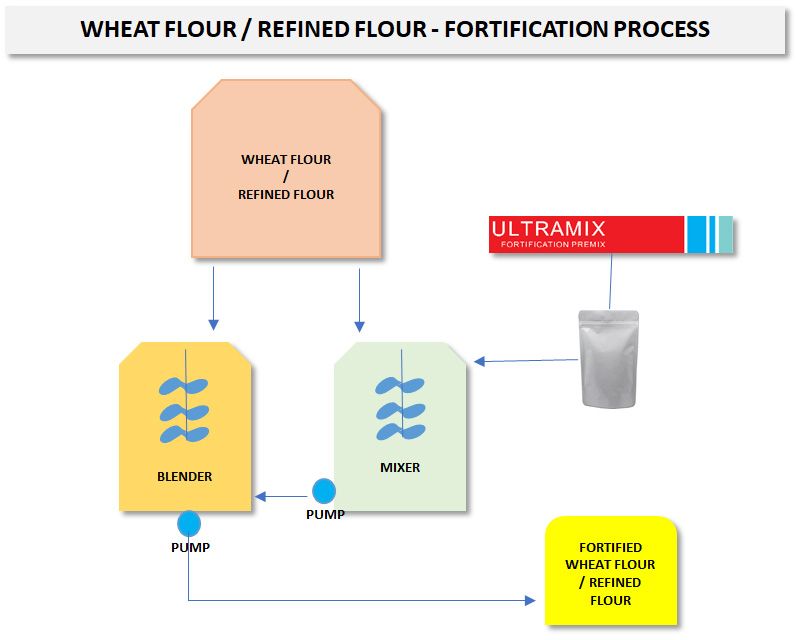
Flour Fortification
The Need
As per National Nutrition Monitoring Bureau (NNMB) survey 2012, the average intake of cereals and millets was 375 GM/CU/day providing >=70% of Recommended Dietary Intake (RDI). Wheat is the staple food for most Indians in the wheat growing areas (North, West and Central India) and is consumed in the form of homemade chapattis or rotis (unleavened flat bread) using custom milled atta (whole wheat flour). For the year 2018-19, wheat consumption is forecasted at 93 MMT. Therefore, wheat flour is a suitable vehicle for fortification to improve the nutritional status of the mass
population.
Advantages of Fortifying Wheat Flour range from it being a safe and effective means of providing nutrients for improving public health excellent vehicle for adding nutrients to the diet as wheat flour is commonly consumed; is a cost-effective method to prevent nutritional deficiencies; and nutrient losses take place during milling of wheat. Further, Iron, Folic Acid and Vitamin B12 added to wheat flour is important for fighting anaemia and enhances blood formation. Fortification helps in adding back these nutrients.